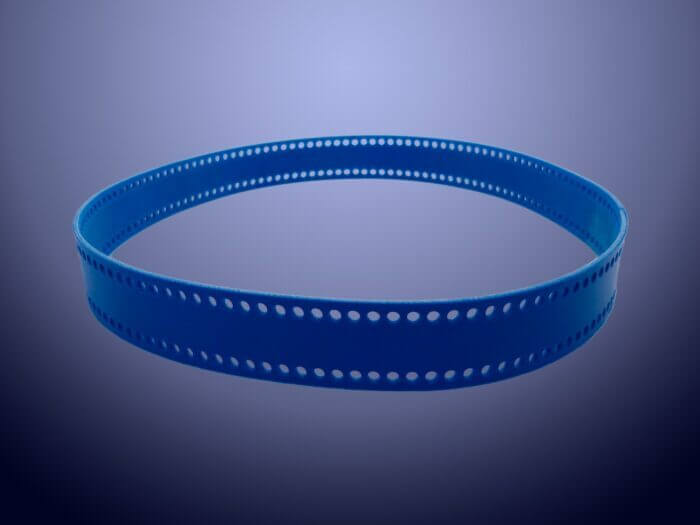
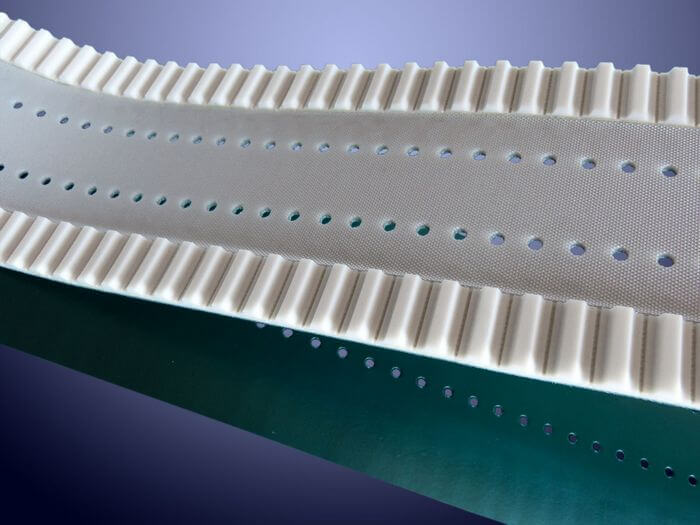
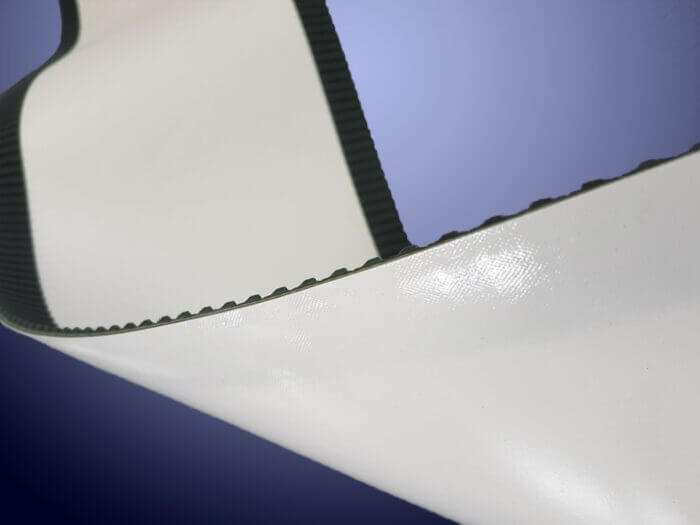
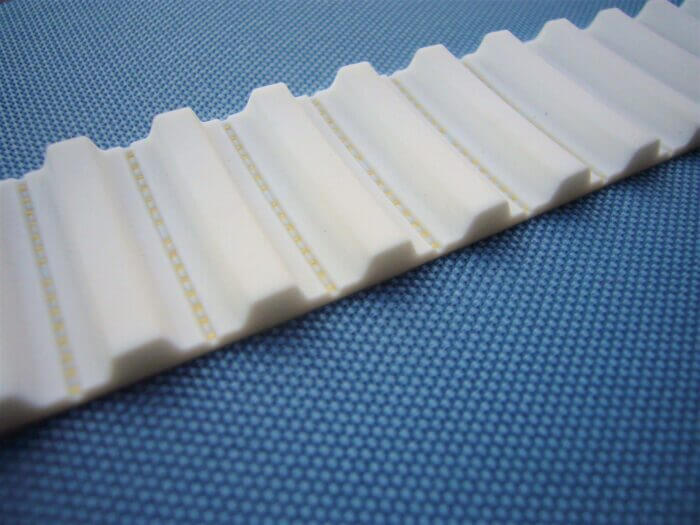
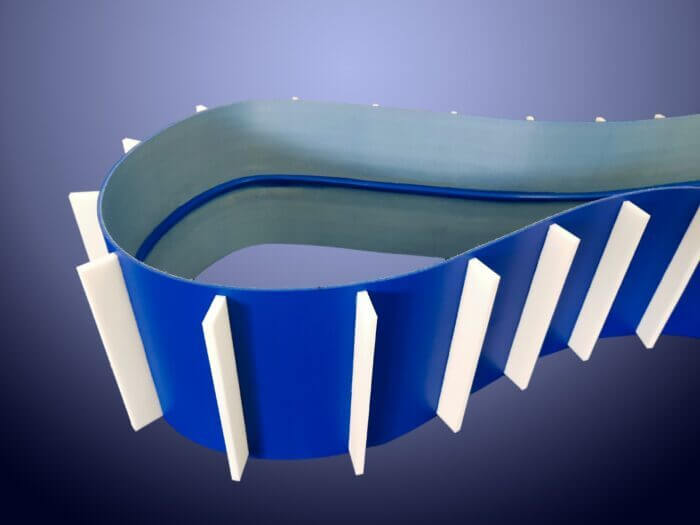
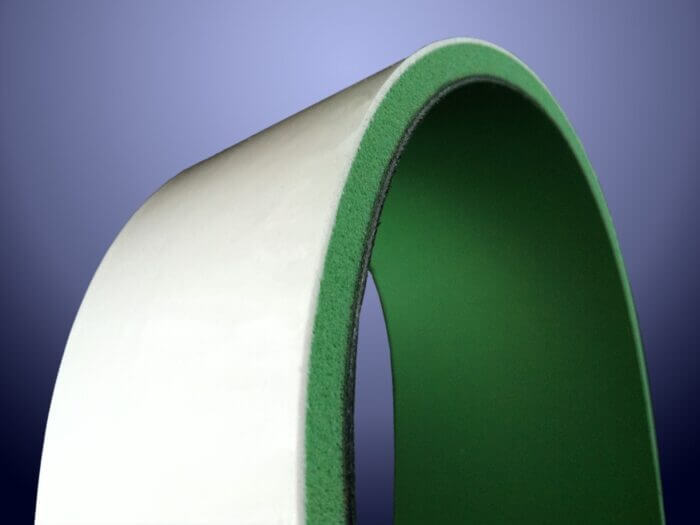
Belts used in conveyor systems represent a versatile product category employed across numerous industries. Thanks to their fabric-based internal structure, they can operate with much smaller pitch diameters than timing belts.
By customizing the back of these belts with attachments, coatings, and specific machining processes, it’s possible to develop conveyor systems perfectly suited to the characteristics of the product being handled. Industries that commonly rely on these specialized transport belts include industrial automation, packaging, paper, textiles, non-woven fabrics, food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and medical sectors.
Synchronous Belts
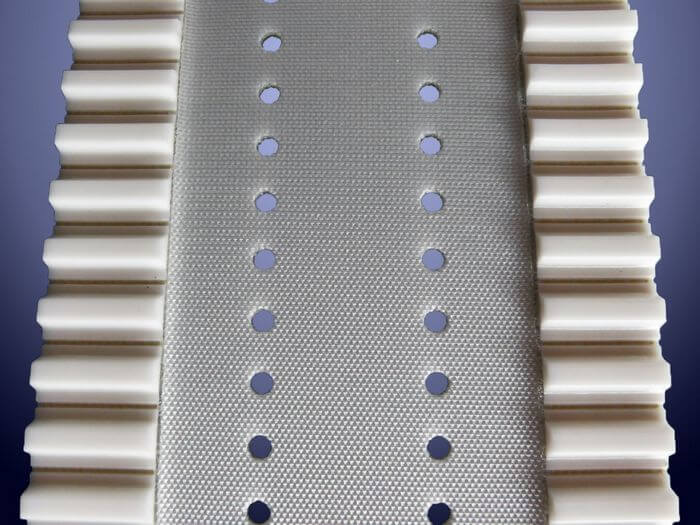
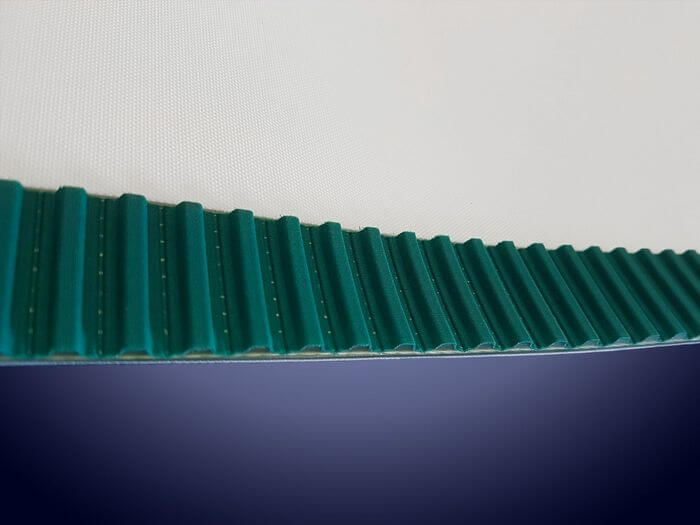
Synchronous belts are advanced systems that merge the benefits of timing belts—such as precise positioning and consistent length—with the flexibility and wide format of smooth belts. This is achieved by milling grooves into the back of polyurethane belts and welding one or more timing belts with Kevlar cords.